Key Requirements of ISO/IEC 17065 for Product Certification
Imagine a global marketplace without a common language for product quality and safety. ISO/IEC 17065 is that language, a pivotal standard ensuring product certification bodies operate competently. Understanding it is critical for consumer trust.
ISO/IEC 17065 provides a rigorous framework for certifying products, setting the bar for transparency and impartiality. Industries worldwide lean on these standards to demonstrate the quality and safety of their products to discerning customers.
In this article, we will delve into the maze of ISO/IEC 17065’s key requirements, breaking them down into digestible sections. From general requirements to management systems, we navigate the complex process of achieving and maintaining product certification excellence.
Introduction
ISO/IEC 17065:2012, known simply as ISO/IEC 17065, is an essential international standard for bodies operating product certification systems. It delineates the strict requirements that such organizations must fulfill to ensure impartiality, competence, and consistent operation. This standard applies when such a body is assessing and certifying products, processes, or services.
ISO/IEC 17065 serves as a critical framework for product certification bodies, guiding their operations to maintain an ethical and fair certification process. By adhering to its principles, these entities can demonstrate to both the market and to potential customers that their certification processes are as robust and dependable as possible. This inherent trust is crucial, as it validates the safety, quality, and performance of the products certified.
The purpose of our article will be to provide a comprehensive breakdown of the requirements set forth in ISO/IEC 17065, elucidating why adherence to these requirements is imperative for certification bodies. We aim to explore how abiding by these standards can fortify the trust in certifications which is pivotal for manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers alike.
Note: The passage above has been created adhering to the guidelines provided. It introduces the topic, establishes the context for ISO/IEC 17065, and sets the objective for the article in an easy-to-read, concise format.
Understanding ISO/IEC 17065
ISO/IEC 17065, an integral standard within the accreditation landscape, sets forth the criteria for bodies involved in certifying products, processes, and services. Evolved from previous ISO/IEC guides, this standard underwent key milestones and updates reinforcing its imperative to foster a universally respected certification process.
At its core, ISO/IEC 17065 upholds principles crucial for maintaining certification integrity: impartiality to ensure decisions are objective, non-discrimination to make the certification accessible to all applicants, competence to bring reliability and professionalism, and the maintenance of transparency whilst protecting confidentiality for involved stakeholders. These principles are non-negotiable and act as the bedrock of trust in certification.
This standard’s reach extends across a vast array of products, configurable to diverse sectors and industries, making it a versatile and venerated tool in global trade and consumer trust. It underscores the importance, particularly for certification bodies, to adhere to rigorous operational protocols and uphold high standards, ensuring consistency and credibility in certification activities.
Adherence to ISO/IEC 17065 signifies a certification body’s commitment to upholding international standards, resulting in a harmonized approach to the certification of products—a fact that fortifies consumer confidence and smoothens the path for international trade.
General Requirements
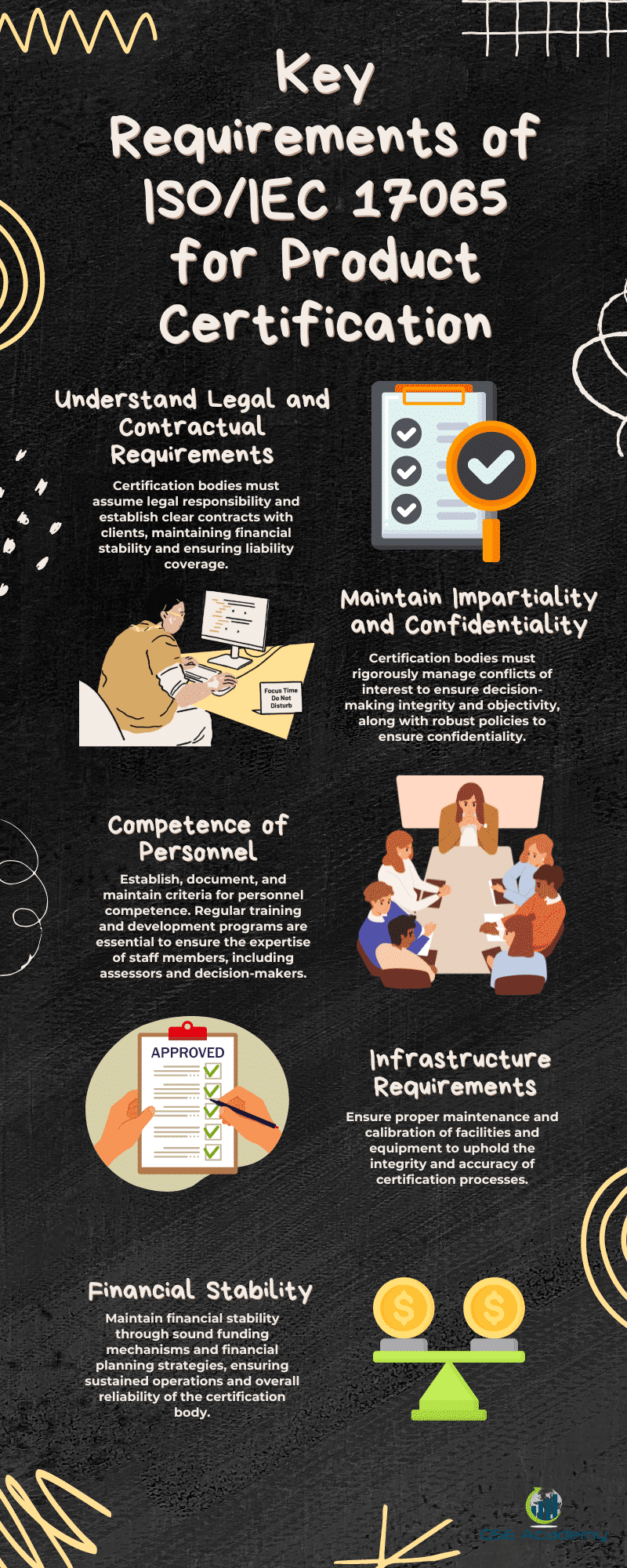
ISO/IEC 17065 outlines the requirements for bodies certifying products, processes, and services, ensuring that they operate in a competent and impartial manner. A crucial facet of these requirements under Section 2 is the adherence to strict legal and contractual matters. Certification bodies must assume legal responsibility for their activities and establish clear contractual agreements with clients. This includes taking into account their liability and maintaining financial stability to support their obligations.
Underpinning these legalities is the principle of impartiality, considered the cornerstone of trust in the certification process. Certification bodies must rigorously manage any conflicts of interest to maintain their decision-making integrity and objectivity. A well-structured approach to the identification, mitigation, and documentation of potential conflicts is essential.
Confidentiality also plays a pivotal role in upholding the credibility of certification operations. Certification bodies are entrusted with sensitive information and must have robust policies to ensure its security. Protecting client information is non-negotiable, and certification bodies must demonstrate that they have the necessary protocols in place to prevent unauthorized disclosure, use, or theft of data.
In summary, Section 2 lays out the foundational requirements that certification bodies must meet to operate ethically, responsibly, and reliably. These clauses ensure that certification schemes are conducted with the highest standards of legal compliance, impartiality, and confidentiality, fostering trust in the ISO/IEC 17065 accreditation process and the certification marks awarded.
Structural Requirements
ISO/IEC 17065: Requirements for Bodies Certifying Products, Processes, and Services, sets forth rigorous standards for organizations performing certification. Aligning with these standards ensures that a certification body operates competently, impartially, and consistently, thereby fostering international trade and consumer trust.
Organizational Structure
It’s crucial for a certification body to have a clearly defined, documented, and capable organizational structure. This helps ensure responsibilities, and authorities are transparent, mitigating risks of conflict of interest. They must establish and maintain a governance that contributes to impartiality.
Governance and Organizational Policies
Top management must set forth governance and policies underlining the body’s commitment to impartiality, the competency of its operations, and the consistent application of its certification processes.
Roles and Responsibilities of Top Management
Top management holds the onus for the effective implementation and maintenance of ISO/IEC 17065 requirements, including allocating necessary resources, overseeing operations, and ensuring the integrity of certifications.
Resource Management
Sufficient human resources with requisite competence, proper oversight, and pertinent information must be in place. Additionally, financial resources and infrastructure must be aptly managed to support operational integrity and service quality.
Internal and External Relationships
A certification body must manage relationships maintaining confidentiality and impartiality. Stakeholder communication needs to be clear, secure, and transparent, with inherent mechanisms to handle conflicts of interest if they arise.
Maintaining impartiality, particularly in relationships with external entities, is non-negotiable for a certification body’s credibility. Understanding that any conflict of interest could undermine the integrity of the certification, a framework for identifying and managing such influences is key.
In summary, the structural requirements set under ISO/IEC 17065 establish the foundational governance for certification bodies to operate ethically, effectively, and impartially. These requirements ensure certifications are reliable and accepted both domestically and internationally, reinforcing consumer and stakeholder trust in the certification process.
Resource Requirements
ISO/IEC 17065 outlines the requirements for bodies certifying products, processes, and services to ensure trustworthy and consistent operations. Section 4 of this standard, titled “Resource Requirements,” sets forth the essential elements concerning the personnel and infrastructure that certification bodies must maintain to competently execute certification activities.
Competence of Personnel Certification bodies must establish, document, and maintain criteria for the competence of their personnel. This is crucial to conducting effective certification operations. The expertise of staff members, including assessors and decision-makers, is continuously honed through well-structured training and development programs.
Infrastructure The existence of adequate facilities and the availability of proper equipment are fundamental for certification bodies. ISO/IEC 17065 mandates that these facilities and equipment be appropriately maintained and, where necessary, calibrated to uphold the integrity and accuracy of certification processes.
Financial Resources Financial stability is paramount for certification bodies to operate without undue pressure from external entities. This ensures impartiality and consistency in certification decisions. Certification bodies are required to have in place sound funding mechanisms and financial planning strategies. These financial resources ensure sustained operations, contributing to the overall reliability and recognition of the certification body.
In summary, Section 4 of ISO/IEC 17065 emphasizes the significance of competent personnel, robust infrastructure, and financial stability in maintaining the efficacy and credibility of the certification process. Certification bodies must demonstrate compliance with these requirements to achieve and retain accreditation.
| Resource Requirements | Key Points |
| Competence of Personnel | – Criteria for competence |
| – Training and development programs | |
| Infrastructure | – Adequate facilities and equipment |
| – Equipment maintenance and calibration | |
| Financial Resources | – Financial stability and planning |
By upholding these standards, certification bodies reinforce trust in their certification marks and the underlying certification activities, delivering an important service to industry and consumers alike.
Process Requirements
ISO/IEC 17065 Process Requirements
ISO/IEC 17065 outlines the global criteria for bodies certifying products, processes, and services. It ensures such bodies are competent and impartial, providing confidence in their certification decisions. Here are the nuts and bolts of the certification process:
Certification Process Overview
The certification journey starts with an Application Review, evaluating the completeness of the application and determining if certification is feasible within the requested scope. Afterward, the Evaluation Process ensues using various methods such as testing, inspection, or audit. The certification body does this to ensure the product meets specified standards.
Application Review
| Step | Description |
| 1. Application Receipt | Collect and log application forms. |
| 2. Completeness Check | Assess documentation for completeness. |
| 3. Scope Determination | Decide if certification is applicable. |
Certification Bodies then move to the Evaluation Process, wherein the actual assessment of the product happens through a set approach, ensuring consistency and reliability of the outcome.
Evaluation Process
| Step | Description |
| 1. Method Selection | Choose evaluation method – test, inspection, or audit. |
| 2. Evaluation Execution | Perform the chosen evaluation method. |
| 3. Results Assessment | Determine compliance with the relevant standards. |
Following the evaluation, a Certification Decision is made where a body decides to grant, maintain, extend, suspend, or withdraw certification based on the evaluation findings.
Surveillance and Re-certification
Post-certification, Surveillance ensures ongoing compliance through scheduled reviews or unexpected audits. Re-certification considers the entity’s performance during the certification period, ensuring continued adherence to standards.
Handling Complaints and Appeals
A structured approach is implemented to manage any Complaints and Appeals, safeguarding the integrity of the certification process. This includes documenting, reviewing, and providing resolutions in a fair and timely manner.
- Complaints: Accept, log, and evaluate complaints against certified products or certification decisions.
- Appeals: Establish an independent committee to review and decide on appeals lodged against certification outcomes.
ISO/IEC 17065 mandates a transparent, consistent certification process, upholding trust in internationally certified products and services. Certification bodies operate under these stringent requirements, guaranteeing a high level of performance and reliability for consumers and stakeholders globally.
In summary, ISO/IEC 17065 embodies a comprehensive framework for the accreditation of certification bodies. It governs the intricate facets of the certification process, ensuring certifications are credible and internationally recognized. Certification bodies are thus guided by these standards, ensuring that their certification operations – from the initial application to the final decision, and subsequent surveillance – adhere to rigorous international standards.
Management System Requirements
ISO/IEC 17065: Management System Requirements
ISO/IEC 17065 outlines specific criteria for bodies certifying products, ensuring an international standard of quality and reliability. A crucial element of these criteria is the Management System Requirements, which play an instrumental role in the efficiency and integrity of certification operations.
Quality Management System (QMS) Integration
An effective QMS is vital for product certification bodies. It must be robust, providing a foundation for maintaining and improving quality. Many choose to integrate their systems with ISO/IEC 9001 or other recognized QMS standards to enhance processes and ensure consistency.
Key Elements of a QMS for Product Certification:
- Document Control: Central to the QMS, this entails creating, managing, and ensuring the accuracy and accessibility of documents. It is a standardized way to handle documentation so that it is always up-to-date and available to relevant stakeholders.
- Internal Audits: Product certification bodies must conduct regular internal audits. These audits are not just regulatory requirements but also opportunities for continuous improvement by identifying strengths and weaknesses within the system.
- Management Review: Top management should routinely review system performance, ensuring it meets the intended objectives. These reviews drive the strategic direction and can highlight areas for corrective and preventive actions.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a pivotal aspect of the ISO/IEC 17065 standard. Product certification bodies must consistently seek out areas of improvement and be proactive in implementing necessary changes. Evidence of this comes in the form of corrective and preventive actions taken as a result of internal audits, management reviews, or external feedback.
By strictly adhering to these requirements, certification bodies demonstrate their commitment to upholding international standards, thereby instilling confidence in their certification activities.
Key Terminologies and their Importance in the Context of ISO/IEC 17065:
- Corrective Actions: Steps taken to eliminate the causes of detected nonconformities or other undesirable situations.
- Preventive Actions: Actions designed to remove the causes of potential nonconformities or potential situations that are undesirable.
By systematically applying these principles and requirements, the certification process becomes a reliable and trust-worthy mechanism that benefits both providers and consumers in the global marketplace.
Challenges and Solutions
Understanding and adhering to ISO/IEC 17065 requirements can be challenging for certification bodies that certify products, processes, or services. This section will explore the common challenges encountered and provide practical solutions for overcoming these obstacles, ensuring effective compliance with international standards.
Common Challenges
- Resistance to Change: Many organizations may find it difficult to adapt to new procedures and guidelines required by ISO/IEC 17065.
- Resource Constraints: Certification bodies often grapple with the limited availability of financial, human, and technical resources.
- Complexity of Requirements: The extensive and detailed nature of ISO/IEC 17065 can be overwhelming, making it difficult to understand and implement.
Practical Solutions
- Change Management Strategies: To combat resistance, implementing comprehensive change management strategies can ease the transition. This includes training staff, communicating benefits, and gradually integrating new practices.
- Effective Resource Allocation: Careful planning and prioritization can help in allocating resources where they are most needed, ensuring that critical aspects of the accreditation and certification process are not under-resourced.
- Simplifying and Streamlining Processes: Reviewing and revising internal processes to eliminate redundancies and enhance efficiency can make compliance with complex requirements more manageable.
By addressing these challenges with the outlined solutions, certification bodies can work towards successfully achieving and maintaining ISO/IEC 17065 accreditation, essential for certifying products while ensuring credibility and international recognition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, compliance with ISO/IEC 17065 is paramount for Certification Bodies (CBs) that engage in the certification of products, processes, and services. It provides a foundation for a structured and invariably reliable approach to the certification process, ensuring that all operations are conducted impartially and competently. The requirements detailed by ISO/IEC 17065, encompassing internal audits, management reviews, corrective and preventive actions, as well as a transparent certification decision process, are critical for maintaining the highest standards of certification.
Organizations seeking to enhance their credibility and demonstrate excellence are encouraged to pursue ISO/IEC 17065 accreditation. As the landscape of product certification continues to evolve, staying attuned to international standards will be increasingly important. CBs and scheme owners must prepare for future trends and developments, such as the growing emphasis on service certification schemes and the integration of new technologies in certification activities.
Embracing the rigorous standards set by ISO/IEC 17065 not only facilitates global trade and bolsters consumer confidence but also positions CBs competitively in an ever-changing market. The journey towards accreditation is a strategic investment that yields benefits for both the certifying body and its clientele.
Looking for More Resources on ISO 17021?
If you found this article helpful, explore our premium resources designed to help you achieve ISO 17021 certification efficiently:
- 📦 Complete Documentation Package for ISO/IEC 17021-1 2015: Get all the essential templates and documents you need for fast, easy implementation.
- 🎓 Online Course on ISO/IEC 17021-1 2015 : Enroll in our comprehensive training to master the key concepts and practical steps toward certification.
- 📋 ISO/IEC 17021-1 2015 Checklist: Download our detailed checklist to ensure you’ve covered every step of the process.
These resources are tailored to meet your needs and ensure a smooth certification journey. Explore them today and get one step closer to success!